In the dynamic global landscape, several distinct megatrends have emerged as pivotal forces reshaping society, the economy, and the environment. These trends are transcending conventional boundaries and leaving an indelible mark on industries, policies, and individual lives.
AI plays a significant role in shaping megatrends, guiding enterprises to incorporate AI into strategic planning for a competitive edge, effective risk management, and innovation potential.Megatrends represent significant, gradual shifts in social, economic, environmental, or technological landscapes. While they take time to develop, once established, these trends have the potential to impact a broad spectrum of activities, processes, and perceptions, often shaping the course of various aspects of life and industry for extended periods, sometimes spanning decades. These underlying forces serve as the drivers of change in global markets and our day-to-day experiences.1
Recognizing these trends is imperative for enterprises, policymakers, and individuals as society propels toward the future. At the forefront of catalyzing megatrends are influencers such as automation, artificial intelligence (AI), cryptocurrencies, remote work, free speech, and environmental sustainability, propelling these trends into the collective consciousness.
AI is instrumental in deciphering megatrends and empowering organizations and policymakers to proactively address associated risk. Rapid advancements in technology, particularly in the realm of advanced AI, are reshaping industries and making automation increasingly widespread. The AI trend is anticipated to experience 37.3% annual growth from 2023 to 2030, a staggering figure that is poised to persist and revolutionize the world.2
AI plays a significant role in shaping megatrends, guiding enterprises to incorporate AI into strategic planning for a competitive edge, effective risk management, and innovation potential. However, organizations must tailor their approaches to AI according to specific needs and contexts. Thus, there can be no singular timeline for implementation.
AI's potential to shape the world across societal, economic, and technological landscapes is significant, and enterprises are urged to focus on AI as a crucial influencer. Institutions are advised to engage in simulation exercises regularly, especially amid the rapid evolution of major influencers, ensuring effective anticipation and adaptation to predict future developments represented by megatrends.
The Identified Influencers
Influencers are phenomena that can drive change and mold the future in significant ways, impacting society, the economy, and various other domains. The identification of influencers on megatrends is grounded in comprehensive research and the identification of key players steering discussions. Figure 1 identifies seven influencers.

The Identified Megatrends
Megatrends refer to large-scale, transformative developments or shifts that significantly impact various aspects of society, economy, technology, and culture over an extended period. These trends have the potential to shape the future, influencing industries, lifestyles, and global dynamics.
Megatrends typically arise from significant technological, demographic, economic, and societal shifts. They are global in scope and have the potential to influence the course of events for many years. Key forces such as technological progress, economic transformations, and demographic shifts play pivotal roles in shaping megatrends, either by propelling, hastening, or facilitating their emergence. These megatrends unfold in waves, each introducing disruptions in various ways.3
Twenty megatrends (figure 2) are identified to be examined against the seven identified influencers (figure 3). The selection of these megatrends is influenced by individual/group perspectives and the current state of affairs, allowing professionals to exercise judgment and make informed determinations.
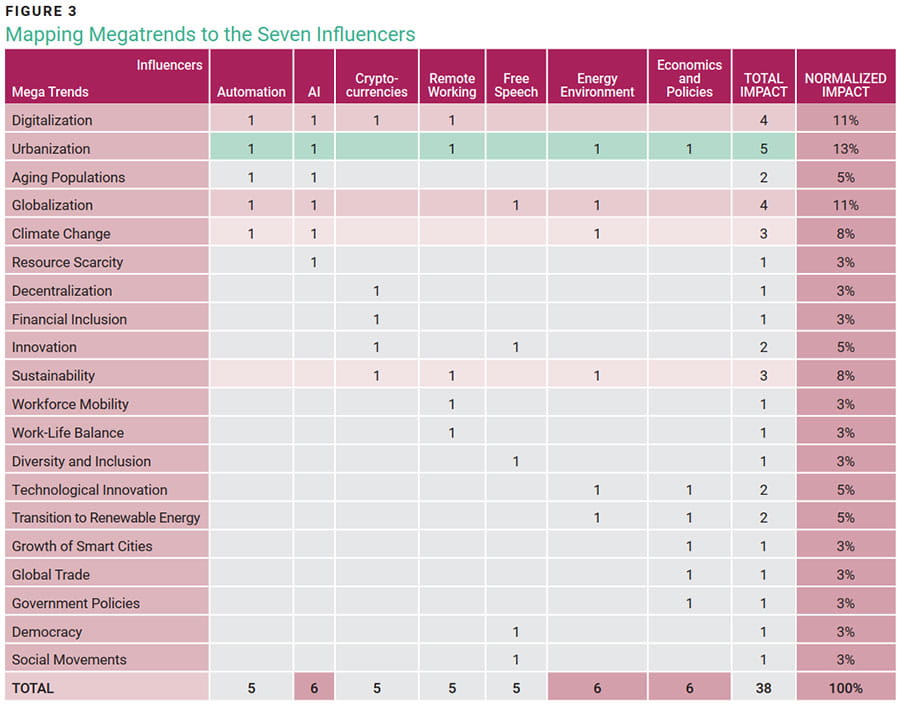
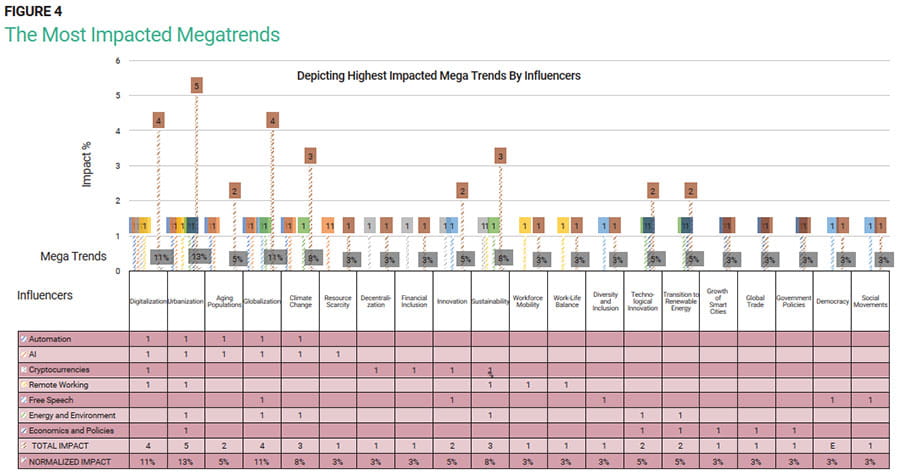
Figure 3 illustrates how an influencer (denoted by 1) impacts different megatrends. The raw normalized impact serves as a way to identify the most impacted megatrends.
In figure 3, megatrends have been associated with identified influencers, and the process of determining which influencer impacts the megatrends involves assigning a numeric value of 1, as carried out by the author. Since this assessment is conducted solely by the author, the author opted for a subjective rating using the simple average method to identify and prioritize the megatrends with the highest impact. To normalize the data, the total impact of each row is divided by the vertical sum of the total impact (38). To achieve an objective and less biased prioritization, it is recommended that the process of choosing the influencers impacting the megatrends is a collective group effort, potentially employing methodologies such as the Delphi4 or the Analytic Hierarchical Process (AHP).5 This collaborative approach aims to mitigate potential biases in the selection process. The stated methodologies are subjective but disciplined by the group discussion.
Top Megatrends and the AI Advantage
AI is poised to be a boon for the cybersecurity sector. Given the frequent occurrences of data leaks, AI is expected to address several key challenges that have long been sources of concern for cybersecurity professionals.6
In 2024, the rapid evolution of the technological landscape is undeniable. The trends in technology for 2024 are set to not only influence the near future but also reshape the fundamental structures of society and business. This presents a distinctive opportunity for technology leaders to strategically chart a course where investments in technology contribute to sustaining success in the face of uncertainties and pressures. To navigate this transformative period, organizations must assess the repercussions and advantages of the latest technological trends, identifying the innovations that will have the most profound impact on their success. Hence, staying well-informed about these trends becomes imperative for anyone seeking to maintain a competitive edge in an increasingly digital world.7
Figure 4 is a graphical representation of figure 3.
The most impacted megatrends that have AI as a primary influencer are identified as:
- Urbanization (13%)
- Digitalization (11%)
- Globalization (11%)
- Climate change (8%)
Thus, detailed analysis will be conducted herein for AI's impact on only the top impacted megatrends: urbanization, digitalization, globalization, and climate change.
AI is a critical influencer in exploring the effects of megatrends due to its ability to handle vast amounts of data, recognize patterns, predict future developments, automate tasks, and provide valuable insights. Integrating AI into the analysis of megatrends enhances the accuracy, efficiency, and comprehensiveness of the examination process.
AI enables the development of predictive models that can forecast future trends based on historical data. This capability is essential for anticipating the trajectory of megatrends and their potential consequences.
AI can automate repetitive tasks related to data collection, analysis, and reporting, allowing researchers and analysts to focus on higher-level thinking and interpretation. This increased efficiency is crucial when dealing with the vast amounts of information associated with megatrends.
Megatrends are dynamic and can change rapidly. AI systems can provide real-time monitoring of relevant data streams, helping stakeholders stay updated on emerging trends and adapt strategies accordingly.
Impact of AI on Urbanization
Given the rapid pace of urbanization, institutions both public and private must strategically plan to accommodate this phenomenon. The impact of AI on urbanization is summarized in figure 5.

The use of smart city technologies is projected to yield annual benefits of up to US$1.7 trillion by the year 2025.8
The typical expenditure of an urban individual can exhibit significant disparities influenced by factors such as income, location, age, lifestyle, and personal preferences. Broadly speaking, urban residents generally allocate more of their spending toward housing, transportation, and food when compared to their counterparts in rural areas. AI can potentially influence this by optimizing resource allocation, providing personalized recommendations, and enhancing efficiency in urban services, thereby affecting spending patterns in these key areas.
According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, in 2021 the average annual expenditure for a consumer unit, which includes families and single individuals, amounted to US$66,928.9 This total encompasses spending on housing, transportation, food, healthcare, entertainment, education, and other miscellaneous expenses.
Impact of AI on Digitalization
According to PwC, AI could contribute up to US$15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030.10 AI influences various industries and applications, impacting digitalization (figure 6).
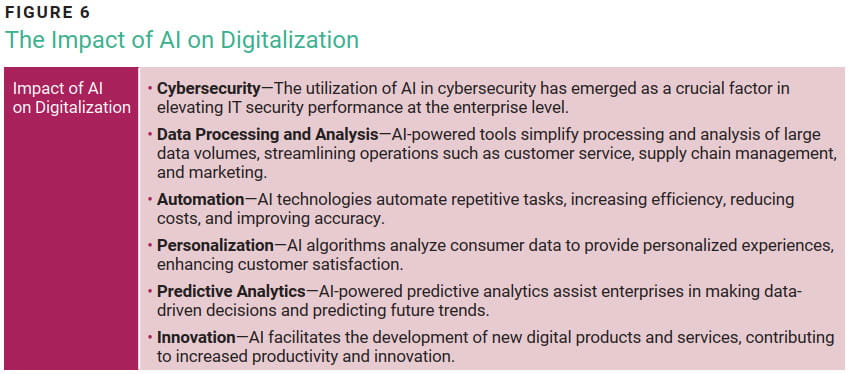
The utilization of AI in digitalization and, in particular, in cybersecurity has emerged as a crucial factor in elevating IT security performance at the enterprise level. AI offers valuable analysis and threat identification, aiding security professionals in minimizing breach risk, prioritizing potential threats, directing incident responses, and preemptively detecting malware attacks.
AI is trending and is becoming increasingly valuable in the domain of governance, risk, and compliance (GRC), aiding organizations in making informed decisions, identifying and mitigating risk, and enhancing compliance efforts. By integrating AI into the workflows of cybergovernance, agencies can proactively prevent or reduce the impact of cyberattacks, efficiently monitor network activity and vulnerabilities, and strengthen access controls for critical data. AI-driven tools automate processes and enable swift identification and resolution of potential risk and issues. Applications of AI in GRC encompass risk assessment, fraud detection, compliance monitoring, contract analysis, anti-money laundering (AML), data privacy protection, regulatory compliance monitoring, and incident response. Leveraging AI technologies empowers organizations to navigate complex regulatory landscapes, protect their interests, and maintain compliance with applicable laws and regulations, while human oversight and governance ensure responsible AI use and overall effectiveness.
Similarly, AI will increasingly and significantly play a role in transforming security operations centers (SOCs), enhancing their capabilities, efficiency, and resilience in countering the evolving landscape of cyberthreats. AI applications in SOCs include advanced threat detection, real-time anomaly detection, user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA), automated incident triage, security incident response automation, threat hunting, malware analysis, predictive analytics, security automation, adaptive security, incident visualization, and contextual analysis. By integrating AI into SOC operations, organizations can bolster their cybersecurity defense, detect threats more effectively, and respond to incidents with greater speed and precision. However, human expertise and governance are essential to ensure the responsible and effective use of AI in SOC environments.
The transformative influence of AI is redefining SOCs and their capacity to provide significant value. Integration of these technologies empowers organizations to enhance the capabilities, efficiency, and resilience of their SOCs, effectively thwarting the ever-changing landscape of cyberthreats.11
Impact of AI on Globalization
McKinsey Global Institute estimates that AI could create US$3.5 trillion to US$5.8 trillion in annual value in the global economy.12 AI’s impact on globalization is summarized in Figure 7.

AI exerts a profound influence across various industries, significantly impacting globalization. In the realm of international trade, AI-powered tools are reshaping global commerce by optimizing supply chain management, reducing costs, and enhancing efficiency. Enterprises can leverage AI to analyze data for identifying suppliers, forecasting demand, and streamlining logistics, thereby expanding their global reach. Additionally, AI-driven language translation tools are breaking down communication barriers, fostering collaboration among individuals from diverse cultures and countries. This not only promotes cooperation but also diminishes language-related obstacles to trade.
In the realm of ecommerce, AI plays a pivotal role in facilitating global transactions by enabling organizations to sell products and services worldwide. AI-driven tools personalize shopping experiences, recommend products, and refine product searches, contributing to the growth of international ecommerce.
Furthermore, AI-powered automation is transforming the global workforce, leading to the replacement of certain jobs while simultaneously creating new opportunities. This shift has intensified competition for employment and altered the dynamics of the global labor market.
In financial markets, the adoption of AI-powered technologies is revolutionizing operations, allowing for more precise trend forecasting and facilitating faster, more efficient trading. This transformative shift is redefining the landscape of financial markets and presenting new prospects for investors and traders alike.
Impact of AI on Climate Change
AI applications are estimated to reduce global greenhouse gas emissions by up to 4% by 2030.13 Quantifying the precise impact of AI on climate change is challenging, but several examples illustrate how AI can contribute to this megatrend (figure 8). First, AI-based systems hold the potential to bolster energy efficiency by optimizing the use of resources such as electricity and fuel, predicting energy demand, and regulating storage systems. This aids in decreasing energy consumption and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. AI can also accelerate the growth of renewable energy by enhancing the efficiency of sources such as solar and wind power, forecasting output, and integrating renewables into the electric grid. This helps reduce reliance on fossil fuels and promotes sustainable energy adoption. In addition, AI can elevate the precision of climate modeling by analyzing vast climate data, simulating complex systems, and providing more accurate forecasts, aiding in understanding and addressing the consequences of climate change. AI also has a potential application in developing carbon capture and storage technologies, thereby improving efficiency and reducing costs by optimizing design and operation. A team of scientists has developed a novel AI-based tool, U-FNO, to enhance the process of locking up greenhouse gases (e.g., CO2) in porous rock formations. This technology aims to improve carbon capture, also known as carbon sequestration, by simulating pressure levels during the storage process.14
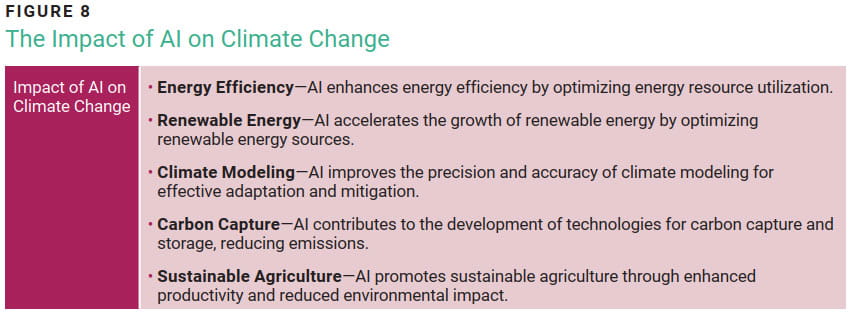
Last, in agriculture, AI can promote sustainability by enhancing crop productivity, optimizing water usage, and reducing chemical usage through the analysis of soil quality, climate patterns, and crop health data. These AI-powered insights enable farmers to optimize operations and minimize environmental impact.
Impact of AI on the Remainder of the Identified Megatrends
AI is a transformative force across diverse aspects of society. In the realm of social movements, AI plays a pivotal role in shaping and amplifying causes by facilitating rapid information dissemination, organizing activities, and fostering communication among activists, thereby enhancing the effectiveness and reach of social movements. In terms of diversity and inclusion, though AI tools can inadvertently perpetuate biases, ethically developed AI has the potential to mitigate bias in hiring processes, promote fairness, and create more equitable opportunities.
Work-life balance also experiences both positive and negative impacts from AI—while automation streamlines tasks and reduces workload, constant connectivity and potential job displacement pose challenges to maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
For the aging population, AI contributes to improved quality of life by assisting in healthcare monitoring, providing companionship through social robots, and enhancing accessibility in daily living.
In the transition to renewable energy, AI proves crucial by optimizing efficiency, aiding in energy storage, and contributing to smart grids, ensuring a stable integration of renewables. Similarly, addressing climate change, AI optimizes energy consumption, aids in climate modeling, and contributes to technologies such as carbon capture, playing a significant role in sustainability efforts. On a global scale, AI transforms the landscape by optimizing supply chains, facilitating cross-cultural communication, and driving ecommerce growth, contributing to more efficient trading in financial markets and influencing the dynamics of international commerce.
AI serves as a driving force in technology innovation by accelerating research, automating processes, and fueling advancements across various industries.
Conclusion
The profound and transformative impact of megatrends on society, the economy, and the environment necessitates vigilant recognition and comprehension for enterprises, policymakers, and individuals to navigate the future effectively. The acceleration of megatrends by influencers such as automation, AI, cryptocurrencies, remote work, free speech, and environmental concerns underscores the importance of examining which influencers will shape these trends, guiding resource allocation and investment strategies.
AI emerges as a critical tool in exploring the effects of megatrends, offering the capability to assess potential risk and develop proactive strategies for mitigation. It can be incorporated into strategic planning for competitive advantages, risk management, and innovation potential. The focus on the most impactful megatrends, including urbanization, digitalization, globalization, aging populations, and climate change, emphasizes the intricate interplay between AI and these transformative shifts.
A collaborative approach to identifying influencers is recommended. This can be achieved by employing methodologies such as the Delphi method or AHP for prioritization and mitigating individual biases. Visual representations of influencers, megatrends, and their interrelationships provide a holistic understanding of the complex landscape.
Delving into the impact of AI on specific megatrends such as urbanization, digitalization, globalization, and climate change illustrates the potential benefits AI brings to diverse domains. From shaping smart cities to enhancing cybersecurity, aiding in governance, cyberrisk and compliance, and transforming security operations against cyberthreats, AI emerges as a transformative force.
There are unprecedented opportunities for innovation, adaptation, and sustainable development at the intersection of AI and megatrends. A collaborative and proactive approach is paramount as institutions and individuals embark on this transformative journey, ensuring the responsible use of AI to harness benefits and address challenges in the evolving landscape of megatrends.
Endnotes
1 Fisk, P.; “Megatrends 2020-2030 … What They Mean For You and Your Business, and How to Seize the New Opportunities for Innovation and Growth,” 6 December 2019, Peter Fisk, https://www.peterfisk.com/2019/12/mega-trends-with-mega-impacts-embracing-the-forces-of-change-to-seize-the-best-future-opportunities/
2 Galov, N.; “Nine New Technology Trends That Will Shape Our Future,” TechJury, 7 February 2023, https://techjury.net/blog/new-technology-trends/
3 Haluza, D.; Jungwirth, D.; “Artificial Intelligence and Ten Societal Mega trends: An Exploratory Study Using GPT-3,” 24 February 2023, https://www.mdpi.com/2079-8954/11/3/120
4 RAND, “Delphi Method,” https://www.rand.org/topics/delphi-method.html
5 Saaty, T.L.; The Analytic Hierarchy Process, McGraw-Hill, USA, 1980
6 Op cit Galov
7 Chugh, S.; “The Top Tech Trends in 2024 and How They Will Shape the Future,” Emeritus, 23 August 2023, https://emeritus.org/blog/tech-trends-2024/#:~:text=Top%2010%20Tech%20Trends%202024%20That%20Will%20Shape,...%208%208.%20Autonomous%20Devices%20...%20More%20items
8 Shaping Tomorrow, “Smart City Futures,” 18 July 2017, https://www.shapingtomorrow.com/home/alert/4165100-Smart-City-Futures
9 US Bureau of Labor Statistics, Consumer Expenditures in 2021, USA, January 2023, https://www.bls.gov/opub/reports/consumer-expenditures/2021/home.htm#:~:text=Average%20annual%20expenditures%20rose%20by,decline%20from%202019%20to%202020
10 PricewaterhouseCoopers, Sizing the Prize: What’s the Real Value of AI for Your Business and How Can You Capitalize?, 2018, https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/issues/analytics/assets/pwc-ai-analysis-sizing-the-prize-report.pdf
11 Singh, C.I.; Nawroth, W.; et al.; “How Do You Leverage AI and ML for SOC Innovation and Enhancement?,” LinkedIn, 27 July 2023, https://www.linkedin.com/advice/0/how-do-you-leverage-ai-ml-soc-innovation#:~:text=AI%20and%20ML%20can%20help%20you%20monitor%20and%20measure%20your,processes%2C%20workflows%2C%20or%20tools.
12 Chui, M.; Manyika, J.; et al.; AI Frontier: Insights From Hundreds of Use Cases, McKinsey Global Institute, 17 April 2018, https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/artificial-intelligence/notes-from-the-ai-frontier-applications-and-value-of-deep-learning
13 PricewaterhouseCoopers, “How AI Can Enable a Sustainable Future,” https://www.pwc.co.uk/services/sustainability-climate-change/insights/how-ai-future-can-enable-sustainable-future.html
14 Salian, I.; “Rock On: Scientists Use AI to Improve Sequestering Carbon Underground,” 8 April 2022, https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/ai-improves-carbon-sequestration/
ROBERT PUTRUS | CISM, PMP, PE
Is a professional with senior management experience in IT, cybersecurity, regulatory and internal controls compliance, managed services, global transformation programs, portfolio and program management, and IT outsourcing. He has published many articles and white papers in professional journals, some of which have been translated into multiple languages. Putrus is quoted in publications, articles, and books, including those used in Master of Business Administration programs in the United States. He can be reached at https://www.linkedin.com/in/robert-putrus-cism-pmp-pe-8793256/.