Artificial intelligence (AI) has applications in various IT domains, including information security (infosec); cloud security; governance, risk, and compliance (GRC); and security operations centers (SOCs). In infosec, AI is useful for threat detection, intrusion prevention, malware detection, and phishing detection, strengthening an enterprise’s overall security posture. In cloud security, AI's swiftness enables early threat detection, and its applications include anomaly detection, real-time threat detection, and predictive security analytics. The use of AI in GRC processes improves risk assessment, fraud detection, compliance monitoring, and incident response. Within SOCs, AI enhances threat detection, incident response, automated triage, and adaptive security measures. Responsible AI deployment, human oversight, and the collaborative integration of AI with human expertise are crucial across all domains. Whether AI will ever replace human beings is worth addressing, highlighting the unique qualities of human intelligence and the ethical considerations surrounding AI.
A holistic approach, merging AI with human expertise and robust governance, alongside continuous monitoring, is essential to effectively combat evolving cyberthreats.AI in cybersecurity brings advantages but also introduces risk such as data dependency, susceptibility to adversarial attacks, and the danger of overreliance. The complexity of deep learning models complicates understanding and addressing potential issues, while scaling AI solutions faces hurdles in complex environments and regulatory compliance. A holistic approach, merging AI with human expertise and robust governance, alongside continuous monitoring, is essential to effectively combat evolving cyberthreats.
AI Applications in Information Security
AI plays a vital role in elevating IT security performance at the enterprise level. By offering analysis and threat identification, AI helps security professionals minimize the risk of breaches, prioritize potential threats, direct incident responses, and preemptively detect malware attacks.1
AI enhances a cybersecurity defense mechanism’s ability to contend with evolving threats. The contributions of AI are multifaceted, including real-time threat detection, stronger intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), proactive malware detection, phishing detection in emails, user behavior analytics, vulnerability assessment, fraud detection in finance, and incident response automation (figure 1). AI is pivotal in fortifying cybersecurity measures and responding effectively to emerging threats.
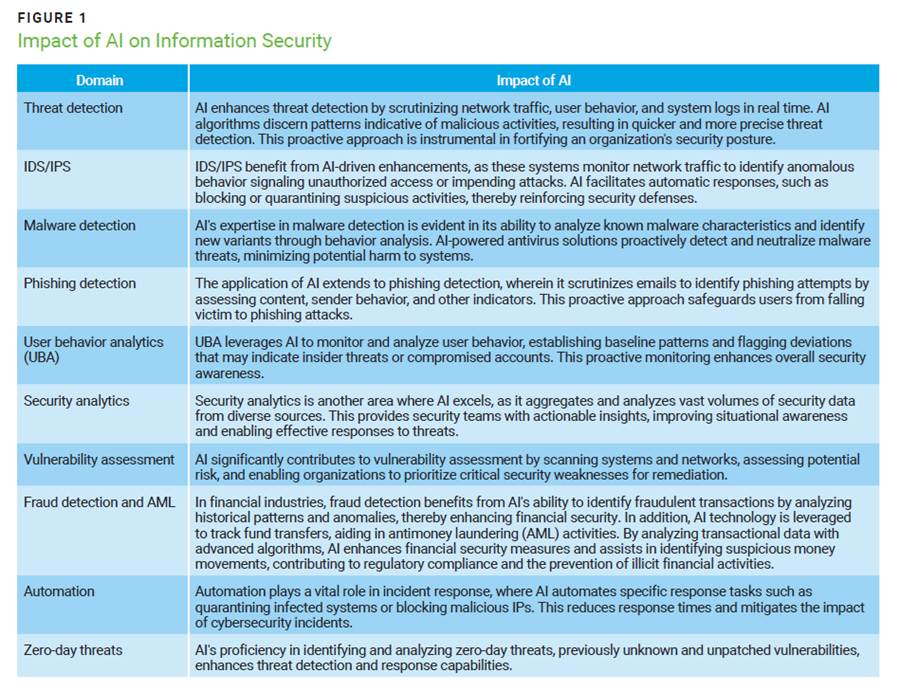
To effectively utilize AI in infosec, input should include diverse data sources, such as network logs, user behavior, and threat intelligence feeds. Quality data is vital for training models to detect anomalies and potential threats accurately. Additionally, contextual information about the organization's infrastructure and security policies enhances AI's understanding and decision-making capabilities.
It is crucial to underscore that AI is not a panacea, and it should work in tandem with human expertise and decision making within cybersecurity operations.Incorporating AI into cybersecurity empowers enterprises, allowing them to stay ahead of rapidly evolving cyberthreats, detect and respond to attacks with agility, and elevate their overall security posture. However, it is crucial to underscore that AI is not a panacea, and it should work in tandem with human expertise and decision making within cybersecurity operations. Human oversight and context-aware analysis remain indispensable components of an effective cybersecurity defense strategy.
AI Applications in Cloud Security
AI offers similar advantages in the realm of cloud security. AI's most prominent benefit in cloud security is its swiftness. Through machine learning (ML) algorithms, AI can recognize typical activity patterns observed in previous cyberincidents, enabling it to learn the early warning signs of similar events. As a result, AI can promptly detect potential attacks or breaches and respond proactively.2
AI has become indispensable in fortifying cloud security, playing a critical role in various aspects of it (figure 2). Anomaly detection powered by AI acts as an early warning system by identifying abnormal activities and potential breaches. User and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) leverage AI to detect suspicious actions. Real-time threat detection, enabled by AI’s processing capabilities, allows prompt identification of and response to security threats. Predictive security analytics use AI to forecast potential risk, allowing issues to be addressed proactively. AI influences cloud access control by enforcing granular access policies, and it enhances cloud data protection through data loss prevention (DLP) systems. Cloud security configuration management, threat intelligence, malware and phishing detection, and automation are additional areas in which AI excels, providing comprehensive insights.
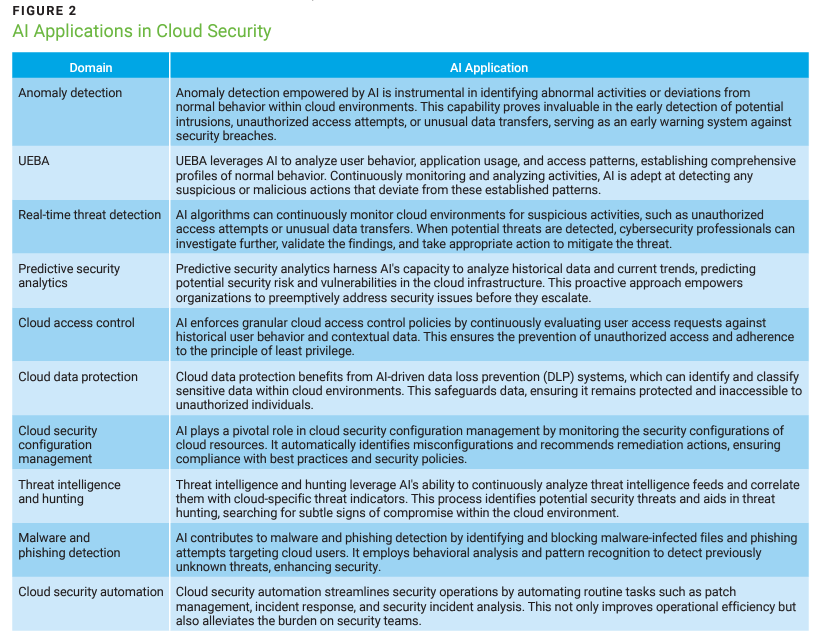
The integration of AI into cloud security bolsters enterprises’ ability to defend against sophisticated cyberthreats, protect their data, and maintain the integrity and av it is imperative to underscore that AI-driven security should work in conjunction with human expertise and governance to ensure the comprehensive and effective safeguarding of cloud resources.
Expanding on the interplay between AI and human values, the collaboration among AI-driven security, human expertise, and governance in securing cloud resources encompasses several key aspects. This includes the continual monitoring of threats by AI algorithms, followed by human review and action. Vulnerability management relies on AI-driven scans to pinpoint weaknesses, with cybersecurity experts then prioritizing responses. AI establishes baseline behavior in cloud environments, while humans analyze anomalies to discern genuine threats from harmless activity. Automated policy enforcement by AI is complemented by human supervision to guarantee compliance with regulations and organizational objectives, facilitating thorough protection and resilience against dynamic threats.
AI Applications in GRC
AI also offers valuable applications in the domain of GRC, helping enterprises improve their decision-making processes, identify and mitigate risk, and enhance compliance efforts.
Integrating AI into governance workflows empowers enterprises to proactively prevent or reduce the impact of cyberattacks. With AI, enterprises can efficiently monitor unusual network activity and entry points, pinpoint potential data vulnerabilities, and strengthen access controls for critical data. AI-driven tools automate and expedite these processes, enabling GRC and security operations teams to identify and address potential threats and issues swiftly and precisely. ML algorithms are capable of detecting patterns and anomalies in data, while natural language processing can analyze unstructured data sources such as emails and social media feeds.3
AI integration into GRC processes provides diverse benefits, improving risk assessment, fraud detection, and compliance monitoring. AI-driven contract analysis tools streamline contract management and aid in AML efforts. AI excels in regulatory compliance monitoring and incident response, as well as in streamlining audit support. AI also contributes insights for strategic decision making in risk management (figure 3).
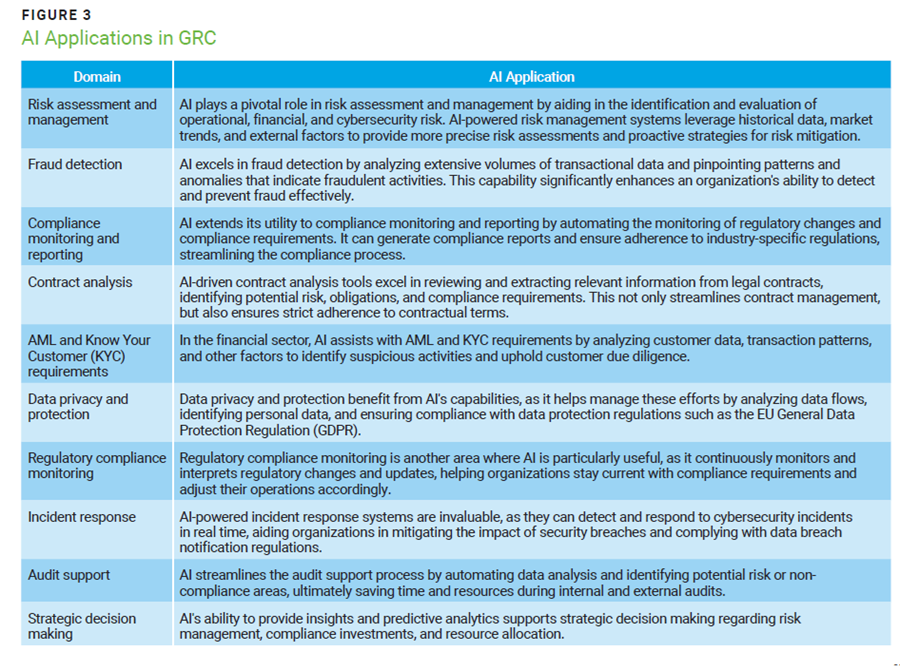
Optimizing AI in GRC involves integrating AI algorithms with GRC platforms to automate risk assessments and compliance monitoring. Furthermore, fostering collaboration between AI systems and human experts ensures accurate interpretation of results and informed decision making.
AI Applications in SOCs
The revolutionary impact of AI and ML is reshaping SOCs and adding to their ability to deliver substantial value. Embracing these technologies bolsters the capabilities, efficiency, and resilience of SOCs, effectively countering the constantly evolving landscape of cyberthreats.4
AI plays a crucial role in improving various aspects of SOCs to strengthen cybersecurity defense, detect threats, and respond to incidents. The incorporation of AI technologies into SOCs leads to a multitude of advantages for bolstering cybersecurity measures.
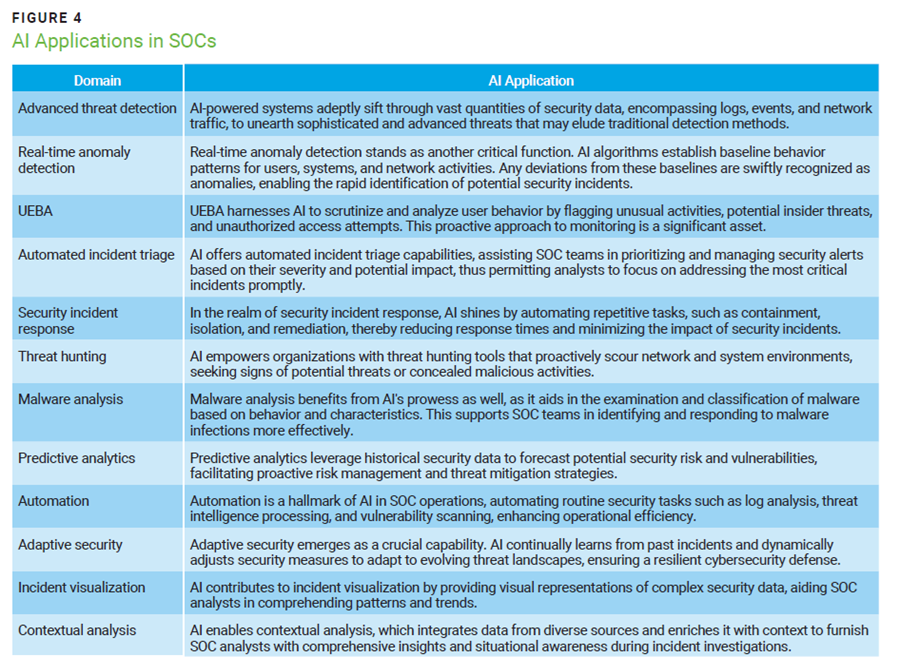
AI enhances cybersecurity with advanced threat detection, real-time anomaly detection, and UEBA. Automated incident triage prioritizes alerts, and AI automates containment and remediation tasks involved in security incident response. Threat-hunting tools proactively identify potential threats. In addition, AI aids in malware analysis and offers predictive analytics for proactive risk management. In SOC operations, AI automates routine tasks, strengthens security measures through adaptive security, aids in incident visualization, and enables contextual analysis (figure 4).
Will AI Replace Human Beings?
The possibility of AI replacing human workers presupposes that AI and humans possess identical qualities and abilities, which is not the case. AI-based machines are speedy, highly accurate, and consistently rational, but they lack intuition, emotions, and cultural sensitivity. These uniquely human qualities are essential for the effective performance of various roles and tasks.5
Emphasizing the importance of human oversight, expert judgment, and robust governance alongside AI integration is crucial for enhancing infosec, GRC, and SOC processes responsibly. This harmonious integration facilitates navigating complex regulatory landscapes, mitigating risk, and making well-informed decisions while complying with laws and regulations. Integrating AI into cyberoperations holds great potential for enhancing cybersecurity capabilities, accelerating threat detection and response, and strengthening overall security postures, but it must be accompanied by human expertise and responsible governance to ensure effectiveness and ethical use.
Despite significant progress, AI has not reached a level where it can completely replace humans. AI is unable to replicate the complexity of human intelligence or evaluate ethical considerations, and it has limited domain expertise. AI excels in specific tasks but lacks the full range of human abilities and consciousness. In certain endeavors and human interactions such as healthcare, AI struggles to simulate aspects of human behavior such as creativity, intuition, and empathy. AI should be viewed as a tool to augment human capabilities, collaborating with humans to solve complex problems. AI can outperform humans in certain areas such as image recognition or data analysis, but it lacks the general intelligence needed to tackle a wide range of tasks that humans can handle effortlessly.
While it continues to transform industries and automate certain tasks, it is unlikely that AI will completely replace human beings in the foreseeable future. However, it is crucial to monitor AI's progress and ensure that its development remains aligned with ethical and societal considerations. The focus should be on responsible and beneficial AI deployment that complements human intelligence and enhances human well-being.
Conclusion
The integration of AI across various domains has the potential to significantly improve enterprises’ ability to counter evolving cyberthreats. AI applications range from threat detection, intrusion prevention, and malware detection to anomaly detection, user behavior analytics, and automated incident response. The incorporation of AI technologies can revolutionize defensive strategies, providing swift and proactive measures to thwart potential breaches. However, it is crucial to emphasize that although AI is a powerful tool, it should work collaboratively with human expertise, maintaining human oversight and responsible governance. Given the unique qualities of human intelligence and the ethical considerations surrounding the use of AI, it is unlikely to replace human beings in the near future. The overall focus remains on responsible AI deployment that complements human capabilities and contributes positively to various aspects of life.
Endnotes
1 Engati, “Top 10 Uses of AI for Cybersecurity,” 21 June 2023, https://www.engati.com/blog/ai-in-cybersecurity#:~:text=Using%20AI%20%20for%20Cybersecurity%20is,malware%20%20attacks%20before%20they%20occur
2 Amos, Z.; “How AI Improves Cloud Security,” AI Journal, 24 October 2022, https://aijourn.com/how-ai-improves-cloud-security/#:~:text=One%20%20of%20AI's%20most%20significant,breaches%20%20and%20take%20action%20sooner
3 Pandey, R.; “The Urgent Need for AI in GRC and Security Operations: Are You Ready to Face the Future?,” ISACA®, 22 March 2023, https://www.isaca.org/resources/news-and-trends/newsletters/atisaca/2023/volume-12/the-urgent-need-for-ai-in-grc-and-security-operations
4 LinkedIn, “How Do You Leverage AI and ML for SOC Innovation and Enhancement?,” 27 July 2023, https://www.linkedin.com/advice/0/how-do-you-leverage-ai-ml-soc-innovation#:~:text=One%20%20of%20the%20main%20benefits,alerts%
5 De Cremer, D.; Kasparov, G.; “AI Should Augment Human Intelligence, Not Replace It,” Harvard Business Review, 18 March 2021, https://hbr.org/2021/03/ai-should-augment-human-intelligence-not-replace-it
ROBERT PUTRUS | CISM, PMP, PE
Is a professional with senior management experience in IT, cybersecurity, regulatory and internal controls compliance, managed services, global transformation programs, portfolio and program management, and IT outsourcing. He has published many articles and white papers in professional journals, some of which have been translated into multiple languages. Putrus is quoted in publications, articles, and books, including those used in Master of Business Administration programs in the United States. He can be reached at robertputrus@therobertsglobal.com or https://www.linkedin.com/in/robert-putrus-cism-pmp-pe-8793256/.
