Introduction
In today's data-driven business landscape, organizations face mounting pressure to deliver real-time insights while managing ever-increasing data volumes and complexity. Zero-ETL has emerged as a transformative approach, fundamentally reimagining how enterprises handle data movement and processing needs. Zero-ETL offers direct data movement capabilities and advanced cloud technologies and allows for the leveraging of modern architectural patterns to enable real-time data access while significantly reducing operational complexity and costs. This paradigm shift represents more than just a technical evolution; it marks a strategic advancement in how organizations can achieve true real-time data integration and analytics capabilities, enabling organizations to respond faster to market changes and customer needs.
Foundational Principles of Zero-ETL
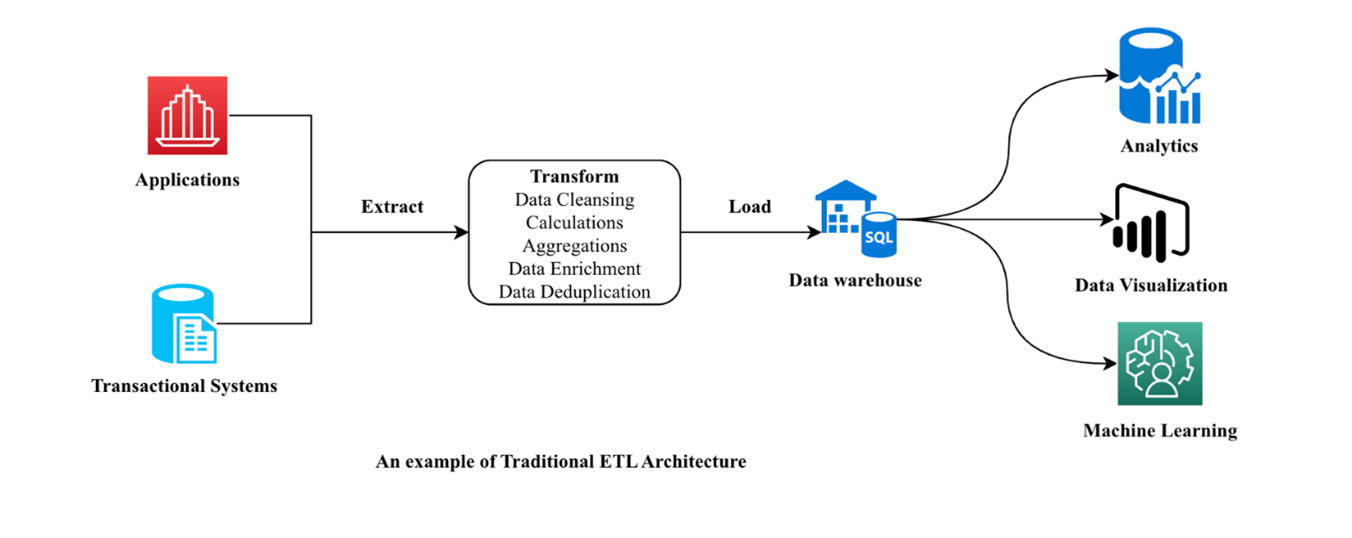
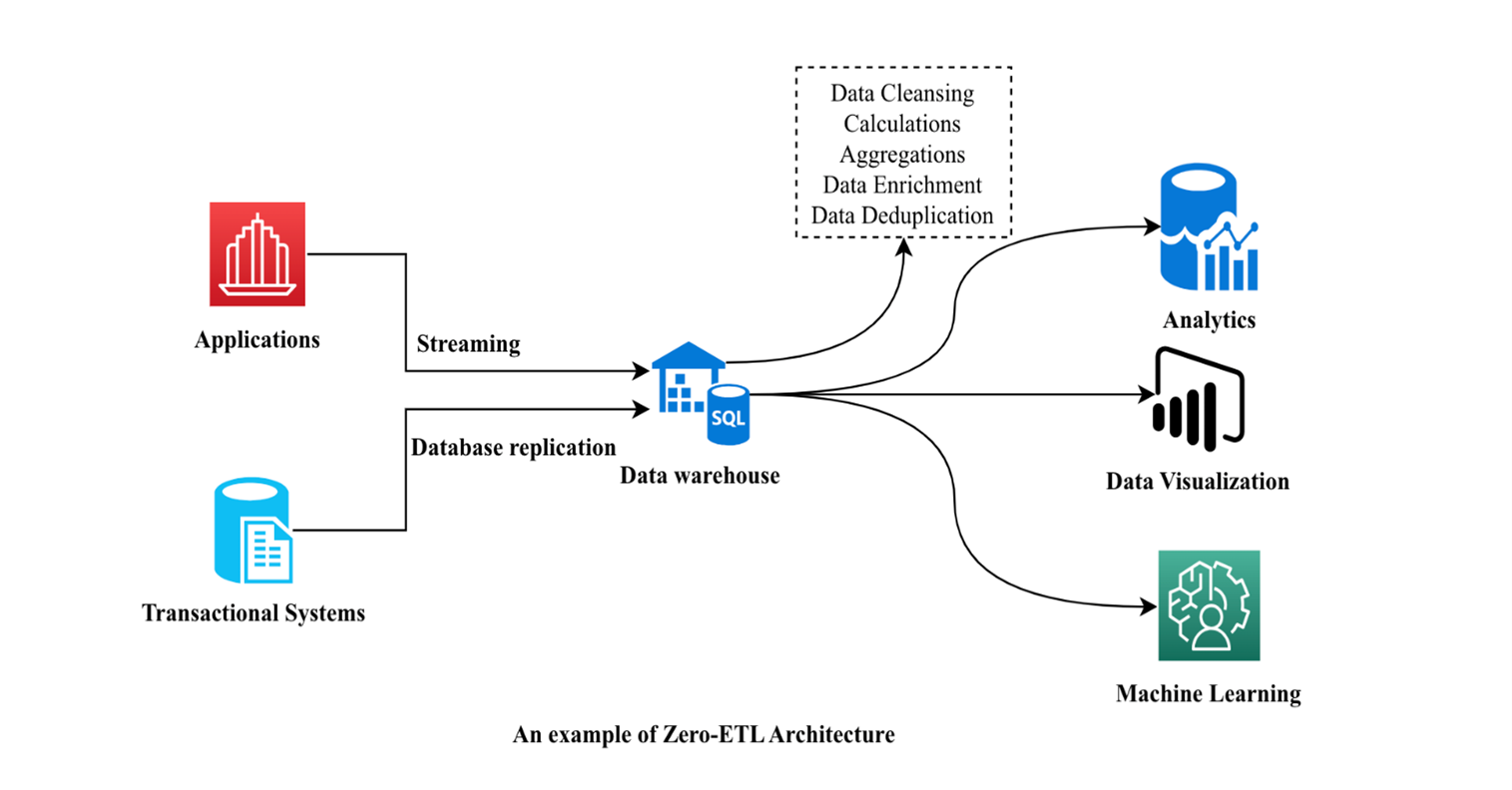
At its core, zero-ETL revolutionizes data integration by eliminating the traditional extract, transform, and load (ETL) pipeline complexities. Unlike conventional ETL processes that require multiple steps and intermediate stages, as seen in figure 1, zero-ETL, as seen in figure 2, establishes direct, point-to-point data movement between sources and targets. This approach defers transformations until query time, enabling immediate data access and analysis while dramatically reducing the latency inherent in traditional ETL workflows. Through advanced technologies such as data virtualization and cloud-native integration services, organizations can unlock the value of their data without the overhead of traditional data engineering tasks.
Figure 1— An Example Of Traditional ETL Architecture
The zero-ETL architecture fundamentally transforms data integration through 3 key innovations: direct data transfer, schema-on-read technology, and cloud-native integration. Direct data transfer eliminates intermediate staging areas and transformation pipelines, enabling immediate data availability through secure, point-to-point movement. Schema-on-read technology defers schema definition until query time, providing unprecedented flexibility in handling diverse data formats without upfront transformation overhead. Cloud-native integration utilizes modern services to optimize performance and scalability, ensuring robust and efficient data processing.
Figure 2—An Example of Zero-ETL Architecture
These foundational elements deliver significant benefits across various industries. Ecommerce platforms can achieve real-time inventory management, financial services can enable instant transaction analysis, healthcare providers can deliver immediate patient data access, and manufacturing operations can optimize real-time production monitoring. This combination of technical innovation and practical benefits makes zero-ETL a compelling solution for organizations seeking to modernize their data infrastructure while maintaining agility and cost effectiveness.1
Dynamic Schema Management in Zero-ETL
A pivotal aspect of the zero-ETL data integration model is its adoption of a schema-on-read approach, distinct from the traditional schema-on-write method.2 In zero-ETL, schema definition is deferred until the data is queried or accessed. This allows data to be stored in its native, often semi-structured format, such as JSON or Parquet, without the need for a rigid schema during ingestion.
The benefits of the schema-on-read approach include the ability to handle diverse data formats, improved agility in adapting to changing data structures, enhanced adaptability to evolving data requirements, and efficient storage utilization by avoiding unnecessary transformations.3
To effectively manage the challenges associated with the schema-on-read approach, organizations must implement robust versioning strategies and schema evolution governance. Implementation will involve:
- Maintaining multiple schema versions to ensure compatibility with historical data
- Conducting impact assessments to evaluate the effects of schema changes on existing data and queries
- Establishing a clear governance framework with defined roles, responsibilities, and approval processes for schema modifications
- Providing comprehensive documentation and ensuring all stakeholders are informed about schema changes
- Validating schema changes through automated testing frameworks
- Conducting user acceptance testing (UAT) to confirm that changes meet business requirements
- Maintaining detailed records of schema changes for compliance and governance purposes
By integrating these practices, organizations can leverage the flexibility of schema-on-read while ensuring data integrity, compatibility, and governance in their zero-ETL environments.4
Real-time Data Access and Processing
One of the essential benefits of the zero-ETL model is its ability to significantly reduce the latency between data generation and data availability for analysis. This is achieved by eliminating the extensive transformation step that is a hallmark of the traditional ETL process. The reduced latency in the zero-ETL approach enables organizations to:
- Respond more quickly to changing customer behavior and market trends
- Provide personalized product recommendations based on the latest purchase data
- Make timely, data-driven decisions to optimize marketing campaigns and promotions
Architectural Advantages and Modernization
Another key benefit of the zero-ETL model is its ability to simplify the overall data integration architecture compared to traditional ETL workflows. In a traditional ETL process, the data integration pipeline typically involves multiple components and complex interactions, which can lead to a convoluted and maintenance-heavy system.5 The zero-ETL approach, on the other hand, focuses on facilitating direct data transfer from source to target, eliminating the need for extensive intermediate steps and components. This simplified architecture offers several advantages, such as reduced complexity, decreased maintenance overhead, improved agility, enhanced flexibility, and cost optimization.6
Economic Benefits and ROI
Zero-ETL delivers significant cost advantages by eliminating traditional ETL overhead and leveraging cloud-based, serverless architectures with usage-based pricing. The simplified architecture reduces maintenance costs by removing separate extraction, transformation, and loading processes while enabling faster time-to-value through real-time data access. Organizations benefit from reduced infrastructure management costs and improved adaptability to changing requirements without expensive system overhauls. For instance, organizations can significantly reduce expenses by replacing dedicated ETL teams and infrastructure with cloud-native services, though actual savings depend on specific workload patterns and data complexity. With zero-ETL integration, some services include fresher data for analytics, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and reporting. Organizations can expect more accurate and timely insights for use cases such as business dashboards, optimized gaming experience, data quality monitoring, and customer behavior analysis. This approach benefits organizations seeking to minimize operational overhead while maintaining agile data integration capabilities.
Best Practices and Implementation
Successful zero-ETL implementation requires a systematic approach and adherence to established best practices across several key areas. Organizations should begin with a comprehensive assessment of their data landscape, including data volumes, variety, velocity, and existing integration patterns. This assessment helps identify suitable use cases for zero-ETL adoption and potential challenges that may need to be addressed. The implementation strategy should follow a layered data architecture approach. These layers include foundation, integration, processing, governance, and monitoring, each playing a crucial role in ensuring successful deployment and operation.
The foundation layer serves as the bedrock of the zero-ETL architecture, providing the necessary infrastructure, security, and governance frameworks. Essential best practices span multiple domains, from data architecture design to operational excellence and security considerations. Organizations must implement clear data organization strategies, define access patterns, and establish robust governance frameworks while maintaining flexibility for future growth. Operational excellence is achieved through comprehensive monitoring systems, automated testing procedures, and detailed documentation, supported by clear incident response protocols. Performance management requires regular baseline measurements, continuous optimization, and proactive capacity planning, while security and governance demand robust access controls, encryption, and compliance monitoring.
Compliance Risk and Governance Challenges
While zero-ETL offers numerous benefits, it also introduces compliance risk and governance challenges that organizations must address. Key concerns include:
- Security vulnerabilities— Direct data movement may expose sensitive data to unauthorized access if proper security measures are not in place.
- Data consistency challenges—Ensuring data consistency across disparate sources can be challenging in a zero-ETL environment.
- Governance issues—The decentralized nature of zero-ETL can complicate data governance and lead to unintended risk.
There are several strategies that organizations can implement to mitigate risk impact:
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing. Implement robust encryption and access controls and conduct regular security audits and penetration testing.
- Implement automated data validation and quality checks.
- Develop a comprehensive data governance framework that includes clear documentation, roles, and responsibilities.
Zero-ETL in Practice
Zero-ETL offers significant advantages in terms of the speed of data access and the simplicity of data integration workflows, however, it does not entirely replace the need for traditional ETL processes in all data integration use cases.
Traditional ETL remains essential for handling complex data transformations, ensuring comprehensive data quality checks, and supporting batch-oriented data processing workflows. Zero-ETL’s focus on direct data movement and deferred transformations makes it less suitable for scenarios requiring extensive data cleansing, enrichment, or consolidation from multiple, disparate sources. Organizations should carefully evaluate their specific requirements, considering factors such as data complexity, transformation needs, and governance requirements when deciding on their data integration strategy. The future of data integration likely lies in a balanced approach that combines the agility of zero-ETL with the robust transformation capabilities of traditional ETL processes.
As organizations increasingly seek to leverage real-time data insights, the adoption of zero-ETL emerges as a pivotal strategy. However, transitioning to this innovative approach requires careful planning and consideration of various factors to ensure successful implementation. 5 steps can guide organizations through the adoption of zero-ETL, addressing key aspects from assessing the data landscape to continuous optimization. These steps include:
- Assess the data landscape—Evaluate data volumes, variety, velocity, and existing integration patterns.
- Identify use cases—Determine suitable use cases for zero-ETL adoption.
- Evaluate challenges—Address potential compliance risk, security vulnerabilities, and governance issues.
- Implement best practices—Follow established best practices for data architecture, operational excellence, and security.
- Monitor and optimize—Utilize comprehensive monitoring systems and continuous optimization strategies.
By following these steps, Organizations can ensure that zero-ETL is implemented strategically and securely.
Zero-ETL in Practice: A Pionex Case Study
Pionex US, a cryptocurrency exchange, faced significant challenges with data processing latency that impacted its ability to provide real-time trading insights. With data delays of up to 30 minutes, the company struggled to help traders respond to rapid market changes. By implementing Amazon Aurora MySQL zero-ETL integration with Amazon Redshift, Pionex US dramatically transformed its data processing capabilities. The solution reduced latency by over 98% (from 30 minutes to less than 30 seconds), cut deployment and maintenance costs by 80%, and decreased overall operational costs by 66%.7 The streamlined architecture also reduced the workload required to create data pipelines by 80%, dropping from a 4-hour, 2-person task to a 30-minute, single-person operation. This transformation enabled Pionex US to provide near real-time analytics for their automated trading bots, enhance risk control, and deliver more timely insights to traders. The success of this implementation has positioned Pionex US to continue innovating with plans to incorporate additional AWS services to further enhance the company's data processing capabilities.
Emerging Trends and Future Directions
The future of zero-ETL looks promising. Advancements such as continuous evolution in cloud capabilities, advanced automation features, and enhanced governance tools are just some of what the future of zero-ETL holds. Implementation trends show the growing adoption of hybrid approaches, an increased focus on real-time analytics, and enhanced security and compliance capabilities. Organizations are also seeing improvements in monitoring and observability tools that support zero-ETL implementations.
Conclusion
Organizational adoption of zero-ETL represents a significant paradigm shift in enterprise data integration, offering real-time data access, reduced latency, and simplified architecture. By leveraging advanced cloud technologies and modern architectural patterns, organizations can achieve real-time data integration and analytics capabilities, enabling faster responses to market changes and customer needs. However, successful implementation requires careful consideration of compliance risk, governance challenges, and the integration of best practices across data architecture, operational excellence, and security.
As the landscape of data integration continues to evolve, a balanced approach that combines the agility of zero-ETL with the robust transformation capabilities of traditional ETL processes will likely emerge as the optimal strategy for organizations seeking to modernize their data infrastructure while maintaining agility and cost-effectiveness.
Endnotes
1 Khademi, V.; “What is Zero-ETL? Introducing New Approaches to Data Integration,” DataCamp, 25 June 2024
2 Stobierski, T.; ”The Advantages of Data-Driven Decision-Making,” Harvard Business School Online, 26 August 2019
3 Stobierski; “The Advantages of Data-Driven Decision-Making.”
4 Stobierski; “The Advantages of Data-Driven Decision-Making.”
5 National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST),NIST Big Data Interoperability Framework: Volume 7, Standards Roadmap (NIST Special Publication 1500-7r1), June 2018
6 Khademi; “What is Zero-ETL? Introducing New Approaches to Data Integration”
7 Amazon Web Services (AWS), “Reducing Latency by Over 98% Using Amazon Aurora and Zero-ETL Integration with Pionex US,” 2024
Shamnad Mohamed Shaffi
Is an accomplished IT professional with over 18 years of experience in data analytics, cloud computing, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Business Intelligence. He specializes in designing and implementing data platforms, analytics solutions, cybersecurity, and governance frameworks. Shaffi empowers organizations through innovative data engineering solutions that enable data-driven decision making and digital transformation.